Social Learning Theory - Web Quest

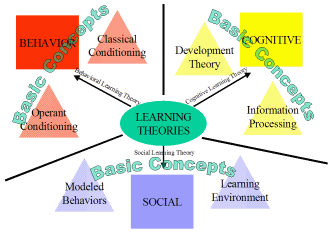
- Behavioral Theory
- Cognitive Theory
- Social Learning Theory
- Introduction
- Task
- Process
- Resources
- Evaluation
- Conclusion
Process
History of theorists and their contributions
Albert Bandura of Stanford University
Bandura completed various research of how people learn by observation. He tested how children learn violent behavior through modeling. He found that parental hostile attitudes had a greater influence on child violent behavior than punishment of the behavior.
One of these projects studied how people's perceptions of their ability to control what they perceive as threats to themselves affect the release of neurotransmitters and stress-related hormones into the bloodstream. A major finding that resulted from these studies was that people can regulate their level of physiological activation through their belief in self-efficay.
He developed a social cognitive theory of human functioning. In this view, people are self-organizing, proactive, self-reflecting, and self-regulating, not just reactive organisms shaped and sheparded by environmental forces or driven by concealed inner impulses.
Critical components /principles
How the Environment Reinforces and Punishes Modeling
- The observer is reinforced by the model.
- The observer is reinforced by a third person.
- The imitated behavior itself leads to reinforcing consequences.
- Consequences of the model's behavior affect the observer's behavior vicariously.
A Contemporary Social Learning Perspective of Reinforcement and Punishment
- Reinforcement and punishment influence the extent to which an individual exhibits a behavior that has been learned.
- The expectation of reinforcement influences cognitive processes that promote learning.
Basic Concepts
Modeling
According to Bandura, many behaviors people exhibit have been acquired through observing and modeling what others do.
Bandura identifies three different types of models:
- Live model
- an actual person demonstrating a particular behavior
- Symbolic model
- a person or character portrayed in a film, television show, book, or other medium
- Verbal instructions
- descriptions of how to behave - without another human being, either live or symbolic, being present at all
Behaviors that can be learned through modeling
- Aggression:
- many research studies show that children become more appressive when they observe aggressive or violent models.
- Morality:
- Many aspects of moral thinking and moral behavior are apparently influenced by observation and modeling.
Conditions Necessary for Effective Modeling to Occur
- Attention
- Retention
- Motor Reproduction
- Motivation
Effects of Modeling on Behavior
- Modeling teaches new behaviors.
- Modeling influences the frequency of previously learned behaviors.
- Modeling may encourage previously forbidden behaviors.
- Modeling increases the frequency of similar behaviors
Characteristics of Effective Models
- The model is competent.
- The model has prestige and power.
- The model behaves in stereotypical "gender-appropriate" ways.
- The model's behavior is relevant to the observer's situation