Social Learning Theory - Web Quest

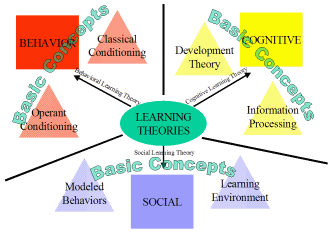
- Behavioral Theory
- Cognitive Theory
- Social Learning Theory
- Introduction
- Task
- Process
- Resources
- Evaluation
- Conclusion
Introduction
Definition of Social Learning Theory and how it applies to learning:
Social learning focuses on the learning that occurs within a social context. It considers how people learn from one another, encompassing such concepts as observational learning, imitation, and modeling. Although many species of animals can probably learn by imitation, social learning theory deals primarily with human learning.... Social Learning theories have behaviorist roots, like cognitivism, but social learning rejects both behaviorism and cognitivism for not taking the environment into consideration.
General Principles of Social Learning Theory
- People can learn by observing the behaviors of others and the outcomes of those behaviors.
- Learning can occur without a change in behavior.
- The consequences of behavior play a role in learning.
- Cognitionn plays a role in learning.
Educational Implications of Social Learning Theory
- Students often learn a great deal simply by observing other people.
- Describing the consequences of behaviors can effectively increase appropriate behaviors and decrease inappropriate ones.
- Modeling provides an alternative to shaping for teaching new behaviors.
- Teachers and parents must model appropriate behaviors and take care that they don't model inappropriate ones.
- Teachers should expose students to a variety of other models.
- Students must believe that they are capable of accomplishing school tasks.
- Teachers should help students set realistic expectations for their academic accomplishments.
- Self-regulation techniques provide effective methods for improving behavior.