Cognitive Learning Theory - Web Quest

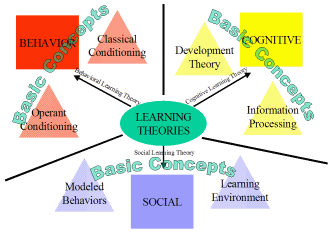
- Behavioral Theory
- Cognitive Theory
- Introduction
- Task
- Process
- Resources
- Evaluation
- Conclusion
- Social Learning Theory
Introduction
Definition of Cognitivism and how it applies to learning:
Cognitivism focuses on an unobservable change in mental knowledge.
Cognitivism came about as a rejection of the behaviorist views. Psychologists believed that mental events, or cognitivism, could no longer be ignored.
General Assumptions of Cognitive Theories
- Some learning processes may be unique to human beings.
- Cognitive processes are the focus of study.
- Objective, systematic observations of people's behavior should be the focus of scientific inquiry, however, inferences about unobservable mental processes can often be drawn from such behavior.
- Individuals are actively involved in the learning process.
- Learning involves the formation of menatal assocaitions that are not necessarily reflected in overt behavior changes.
- Knowledge is organized.
- Learning is a process of relating new information to previously learned innformation.
General Educational Implications of Cognitive Theories:
- Cognitive processes influence learning.
- As children grow, they become capable of increasingly more sophisticated thought.
- People organize the things they learn.
- New information is most easily acquired when people can associate it with things they have already learned.
- People control their own learning.